In a world where data privacy has become a top concern for consumers, businesses must adapt their marketing strategies to stay compliant with ever-evolving regulations. With the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), cold calling practices have undergone significant changes, raising questions for sales and marketing professionals.
How can businesses continue to reach out to potential clients without violating GDPR rules? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of cold calling GDPR and provide valuable insights on how to stay compliant while still leveraging cold calling as an effective marketing tool.
Key Takeaways
Understand GDPR and its impact on cold calling to remain compliant
Adopt GDPR-compliant strategies such as TPS/CTPS screening, providing opt-out options, and developing privacy policies
Manage data securely while conducting regular audits and reviews to ensure compliance with regulations.
Understanding GDPR and Its Impact on Cold Calling

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has introduced a new era of data protection for European citizens and businesses operating within the European Union. Organizations must become well-versed with the GDPR and its impact on cold calling practices. Falling out of compliance with GDPR can lead to hefty fines, which could amount to 4% of a company’s global annual turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
We will delve into the central ideas of GDPR and its influence on cold calling activities.
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of rules governing the processing of personal data of European citizens, even for non-European companies. Giving EU citizens greater control over their personal data and safeguarding their fundamental privacy rights is the primary purpose of GDPR. Non-compliance with GDPR regulations can result in severe penalties, making it crucial for businesses to be aware of their obligations and ensure their marketing strategies, including cold calling, align with GDPR requirements.
GDPR grants EU citizens several rights, such as:
The right to be informed
The right of access
The right to rectification
The right to erasure
These rights ensure that businesses pursue legitimate interests while respecting the privacy of individuals. Organizations involved in cold calling must comprehend the legal grounds for processing personal data under GDPR and put in place suitable measures to guarantee compliance.
How Does GDPR Affect Cold Calling?
Cold calling involves making unsolicited calls to potential clients, a common practice in sales and marketing activities. GDPR affects cold calling by requiring businesses to have a legal basis for processing personal data, such as consent or legitimate interests. Businesses must comply with GDPR rules to evade potential fines and safeguard the rights and interests of the individuals they contact.
The legal basis for cold calling under GDPR is legitimate interest. This allows businesses to make sales calls as long as they respect the rights and interests of the individuals being contacted. For example, a business can ensure their legitimate interests are protected when engaging in cold calling if an individual has previously indicated their willingness to receive other forms of communication from them, such as signing up for their email list. This could be seen as an indication that the person would not be averse to receiving a phone call, making cold calling allowed in certain circumstances.
Key Legal Bases for Cold Calling under GDPR

Cold calling under GDPR relies on two key legal bases: explicit consent and legitimate interests. Both legal bases require businesses to take specific actions to ensure they stay compliant with GDPR regulations while engaging in cold calling activities.
We’ll delve deeper into these legal bases.
Explicit Consent
Explicit consent entails obtaining clear and specific authorization from the individual for marketing purposes, which does not typically involve cold calling. Explicit consent is vital to comply with data protection regulations since not obtaining it can lead to fines and other penalties. Consent must be expressly confirmed in either written or spoken form.
However, obtaining explicit consent for cold calling can be challenging, as it may be difficult to prove that an individual has willingly given their permission for such communication. Businesses must record when and how consent was secured and provide a simple, reachable method for individuals to revoke their consent whenever they choose.
Legitimate Interests
Legitimate interests provide flexibility for businesses in processing personal data for direct marketing purposes, including cold calling, as long as they do not supersede the rights and interests of the data subject. Recital 47 of GDPR clearly indicates that direct marketing can be considered a legitimate interest. However, businesses must carefully consider the interests of the individual being marketed to in comparison to their own.
To determine whether legitimate interests can be used as a legal basis for cold calling, businesses must conduct a “balance test” that weighs their right to conduct operations against the prospect’s right to not receive calls. Businesses must document their legitimate interests assessment (LIA) to exhibit their adherence to GDPR, proving their responsible conduct and consideration of the impact of their processing activities on the individuals they contact.
Adopting GDPR-Compliant Cold Calling Strategies

To ensure GDPR compliance in cold calling, businesses should adopt strategies such as TPS/CTPS screening, providing clear opt-out options, and developing transparent privacy policies. Implementing these strategies will help businesses avoid potential penalties and ensure that their cold calling practices remain in line with GDPR regulations.
We’ll examine these strategies in more depth and how you can implement them in your business with the help of your sales and marketing teams.
Screening Against TPS/CTPS
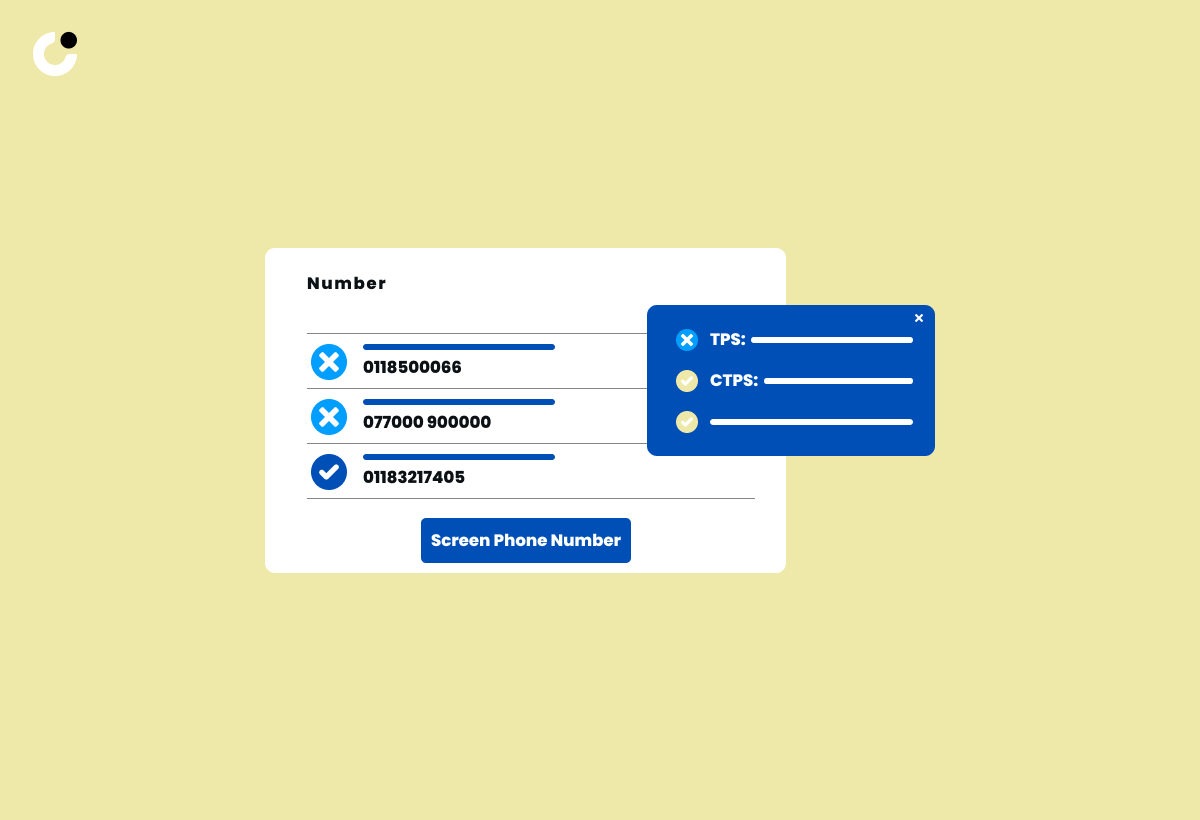
Conducting TPS/CTPS screening enables businesses to ensure that they are not contacting individuals who have registered to opt out of receiving unsolicited calls. The Telephone Preference Service (TPS) is a service in the UK that enables individuals to register their preference to opt out of receiving unsolicited marketing calls. Organizations may incur a fine of up to £500,000 for making an unsolicited call to a consumer registered with the TPS.
To stay compliant with TPS regulations, businesses should regularly screen their contact lists against the TPS and CTPS registers and ensure they do not call phone numbers registered with these services without prior consent. This will help businesses avoid potential penalties and maintain a positive reputation with their target audience.
Providing Clear Opt-Out Options

Providing clear opt-out options allows individuals to easily withdraw their consent or object to further marketing communications. Businesses should make it easy for individuals to revoke their consent or express their objection to further marketing communications by including prominent opt-out options in all marketing materials and communications.
Failure to provide easy opt-out options can result in fines and other sanctions. To ensure compliance with GDPR, businesses should regularly review their opt-out procedures and ensure they are easily accessible and user-friendly for their target audience.
Developing Transparent Privacy Policies

Developing transparent privacy policies is essential to ensure that individuals are aware of how their personal data is being handled and their rights in accordance with GDPR. A transparent privacy policy should clearly explain how the business collects, processes, and stores personal data, as well as outline the rights of data subjects under GDPR.
By creating and maintaining transparent privacy policies, businesses can build trust with their target audience and demonstrate their commitment to protecting the privacy of individuals. This can lead to a better reputation and increased customer loyalty in the long run.
Navigating B2B vs B2C Cold Calling Scenarios
Different rules apply to B2B and B2C cold calling scenarios under GDPR, making it important for businesses to understand the distinctions and ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
In this section, we’ll dissect the distinctions between B2B and B2C cold calling, guiding businesses on how to navigate these scenarios while maintaining GDPR compliance.
B2B Cold Calling

B2B cold calling can be classified under “legitimate interest,” which allows businesses to make sales calls as long as they respect the rights and interests of the individuals being contacted. However, businesses must still ensure compliance with GDPR regulations.
In addition, under the Privacy and Electronic Communications Regulations (PECR), businesses must not call phone numbers registered with the Corporate Telephone Preference Service (CTPS) or the Telephone Preference Service (TPS) without prior consent for marketing calls.
To stay compliant with GDPR and PECR regulations, businesses should:
Carefully consider their target audience’s rights and interests
Obtain explicit consent when necessary
Ensure they do not call phone numbers registered with the TPS or CTPS without prior consent
By following these guidelines, businesses can engage their sales teams in B2B cold calling and cold emailing while respecting the privacy of their potential clients.
B2C Cold Calling

B2C cold calling requires explicit consent, making it more difficult for businesses to engage in this practice without violating GDPR rules. Businesses must obtain explicit consent from customers prior to making any cold calls, as well as provide clear opt-out options and establish transparent privacy policies.
To ensure compliance with GDPR regulations when conducting B2C cold calling, businesses should take the following precautions:
Obtain explicit consent from individuals before making any cold calls.
Document the consent process, including the date, time, and method of obtaining consent.
Review data storage and security measures to protect customer data.
Regularly audit and review processes to identify and address potential compliance issues.
Managing Data and Ensuring Compliance

Proper data management and regular audits are essential for maintaining GDPR compliance in cold calling. Alongside the earlier discussed strategies, businesses should also prioritize:
Data storage and security
Carrying out consistent audits to pinpoint potential compliance issues
Verifying that their practices align with GDPR regulations
In this section, we’ll delve into the significance of data management and routine audits in maintaining GDPR compliance for cold calling activities.
Data Storage and Security
Data storage and security measures must be in place to protect personal data from unauthorized access, loss, or damage. It is imperative that organizations ensure data is stored securely and access is restricted to only authorized personnel. Additionally, to process data effectively, it should be encrypted and backed up on a regular basis.
For both B2B and B2C cold calling scenarios, it is essential that businesses take appropriate measures to store and secure data in accordance with GDPR regulations. Failure to implement proper data storage and security measures can result in severe penalties and damage to the business’s reputation.
Regular Audits and Reviews

Regular audits and reviews help businesses identify potential compliance issues and ensure that their cold calling practices remain in line with GDPR regulations. Routine audits and reviews should encompass an evaluation of the data gathered, the techniques utilized to acquire it, and the systems employed to store and safeguard it.
By conducting periodic audits and reviews, businesses can not only identify potential compliance issues but also enhance their processes and procedures to provide a better experience for their target audience. This proactive approach to maintaining compliance can help businesses avoid costly fines and protect their reputation in the long run.
Summary
Cold calling remains a powerful marketing tool, but GDPR has undoubtedly changed the landscape. By understanding the nuances of GDPR and its impact on cold calling, businesses can adopt compliant strategies and avoid potential penalties. Implementing key legal bases such as explicit consent and legitimate interests, adopting GDPR-compliant strategies like TPS/CTPS screening and providing clear opt-out options, and navigating the differences between B2B and B2C cold calling scenarios are all essential steps in maintaining GDPR compliance.
In conclusion, it’s crucial for businesses to stay informed and proactive in their approach to GDPR compliance in cold calling. By adhering to the guidelines discussed in this blog post and regularly reviewing their processes, businesses can continue to leverage cold calling as an effective marketing tool while respecting the privacy and rights of their target audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is cold calling allowed in EU?
Under GDPR, cold calling is allowed with explicit consent from the prospect and a legitimate reason for contacting them. Businesses must also provide individuals the option to opt out of future calls.
Do cold emails violate GDPR?
Cold emails do not violate the GDPR, as it is applicable to how companies handle the data of individuals rather than interactions with other businesses and organisations.
What are the 3 C's of cold calling?
Successful cold calling requires research and preparation. To be successful, consider the 3 C's – Company, Contact, and CRM.
Does GDPR apply to cold calling?
Yes, GDPR applies to cold calling as it affects how businesses collect, store and process personal data which may be used for these activities.
What are the key legal bases for cold calling under GDPR?
The key legal bases for cold calling under GDPR are explicit consent and legitimate interests.

